The Nucleus Accumbens: A Learning, Motivation, and Pleasure Center


Written and verified by the psychologist Valeria Sabater
Finding the motivation to reach a goal. Despite having failed, believing that further efforts are worth the trouble. The intense pleasure of a kiss. The delight of enjoying your favorite dish. All of these things that are so decisive and important in your daily life are managed by the nucleus accumbens. This area of your sophisticated brain is as interesting as it is exceptional.
Most people don’t know about the very existence of certain regions of the brain until someone they know suffers an accident. However, it’s very important to learn a little more about how your brain functions under normal circumstances. Understanding the function of each region of the brain will allow you to understand your own behavior, motivation, and impulses.
Each brain hemisphere has a nucleus accumbens. They shape your complex reward system. Thanks to this area of the brain, you feel pleasure, lay down new pieces of knowledge, and find the motivation you need for your daily life.
The nucleus accumbens is that fascinating brain structure that’s the foundation of your pleasure and reward system. Without it, you’d lose the strength, release, and unstoppable energy that make you human. All human beings strive to meet their personal goals, emotional goals, sexual needs, the desire for knowledge, or other motivators.
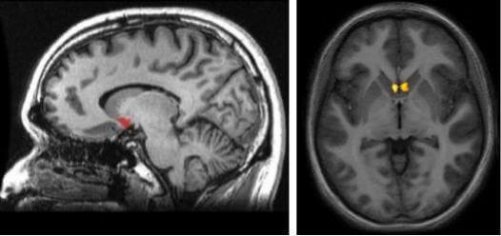
What is the nucleus accumbens?
The nucleus accumbens is a brain region that few people know about. Even the field of neuroscience still has many questions it. We know that its primary function is to activate the motivational system. Beyond just activating that system, it drives behavior. It turns that will, that rush of optimism, and that thirst for victory you often feel into behavioral responses.
Now you might be asking yourself where this brain structure is located. In order to conceptualize it, visualize the subcortical (under the cortex) area right at the connecting point between the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the septum. One of the most significant aspects of the nucleus accumbens is its location, as it’s a part of a dopaminergic pathway of the brain. This is the so-called mesolimbic pathway. It’s in charge of stimulating you whenever your brain believes you’re undergoing pleasurable and gratifying experiences.
Now, as we indicated previously, this structure has a few secrets that puzzle neurologists. Even until recently, experts believed the nucleus accumbens was only linked to gratifying experiences. However, today we know that it’s also connected to unpleasant situations. When you encounter something you don’t like, the nucleus accumbens “activates” motivation to escape from that situation.
Thus, it also plays a pivotal role in your drive for survival, as it directs you toward what benefits you and keeps you away from what might harm you.

Neurobiology of the nucleus accumbens
Each of the brain hemispheres has its own nucleus accumbens. That way, the reward system managed through dopamine reaches each part of the brain. This structure is also part of the basal ganglia. As such, one of the most significant characteristics of the nucleus accumbens is the extent to which it’s connected to other parts of the brain.
In fact, its most significant connection is the one it has with the limbic system. Remember that this system is composed of many different structures: the thalamus, the hypothalamus, and the amygdala. The latter is responsible for the regulation of your emotional world.
Now let’s talk about how the nucleus accumbens actually establishes these significant links by means of its sophisticated anatomical structure.
1. Shell
This is, without a doubt, the most interesting part of the nucleus accumbens. Through the shell, it establishes connections with the limbic system as well as the frontal lobe. This part actually works as a bridge. It receives and sends information. At the same time, it obtains and regulates quantities of dopamine, serotonin, glutamate, etc.
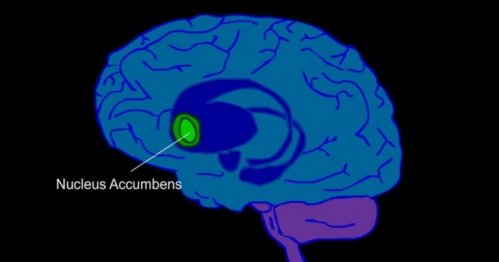
2. Core
This is the heart of the nucleus accumbens. What this region of the brain does is manage motor function through its connection with the basal ganglia, the substantia nigra, and the motor cortex.
The interesting thing about this area is that it activates most of the emotionally-significant actions and movements. That is to say, the nucleus accumbens is behind every time you feel motivated to get up from the couch to do something.
What are the functions of the nucleus accumbens?
We already know that the nucleus accumbens controls motivation, pleasure, and triumph and sets things into motion. However, it also has many other functions:
- It helps us with planning. Due to its connection with the cerebral cortex, it allows us to create goals and road maps.
- This structure helps us evaluate situations. The nucleus accumbens is also linked to your emotional memory. As such, it helps you analyze certain situations to make certain changes, set your efforts toward a goal, or decide whether it’s best to delay certain challenges or goals.
- It helps you learn and integrate new information. Motivation and learning go hand and hand. In fact, the simple act of understanding, integrating knowledge into your brain, and memorizing things would have no sense without the emotional component that the nucleus accumbens is involved in.
- Sex and nutrition. This structure isn’t the only one related to pleasure. However, it plays a key role (as we already know) in motivation and the neurochemical reward system. This is due to the fact that it’s located in a dopaminergic pathway. Remember that dopamine is a neurotransmitter involved in pleasure, happiness, and addiction.
In conclusion, the brain never ceases to amaze us. This organ is a perfect piece of machinery where each small area has a significant function. Nevertheless, no part of the brain works on its own. All the brain’s parts are interconnected and depend on each other to work together in fascinating harmony. The nucleus accumbens is an amazing part of this fascinating machine.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








