Endocannabinoids, the Marijuana of Your Brain

Written and verified by the psychologist Valeria Sabater
Endocannabinoids play a role in memory, rest, reproduction, pleasure, and even stress reduction. They’re fascinating molecules that your body produces to modulate the endocannabinoid (ECS) system. You might be rather surprised to know that your body is actually flooded with these chemicals.
When it comes to biology and neurochemistry, nothing happens coincidentally. In fact, these tiny molecules form a key part of your brain’s reward system. Thanks to them, you carry out your daily tasks. Furthermore, any imbalance in their production can completely alter your feelings of well-being. Recent studies show that any endocannabinoid alteration can intervene in stress and anxiety.
Although these elements are endogenous and produced by the brain, they’re also found in nature. As a matter of fact, you find them in the marijuana plant. You actually have your own endocannabinoid factory.
What are endocannabinoids?
Endocannabinoids are basically lipid molecules (fats) that are essential in neuron communication.
Today, scientists have only identified two types: anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG). When they act on endocannabinoid receptors, they regulate multiple basic processes in your daily life. These include memory, learning, sleep, appetite, and even mood.
However, they also play another essential role. AEA and 2-AG modulate your brain’s reward circuits. They do this by stimulating dopamine production. This means they don’t only regulate your motivation but they also intervene in your feelings of pleasure.
What do they do?
Although scientists have only identified two types of endocannabinoids so far, they feel that there are probably more, given their multiple functions.
Endogenous cannabinoids are natural neurotransmitters. In other words, they act as chemical messengers in the body and send signals between nerve cells.
Their functions are:
Energy regulation
They intervene both in rest and activity. In fact, they promote sleep and also activate your motivation so you experience pleasure when working towards a goal.
Appetite stimulation
Appetite is one of the most important physiological processes that the endocannabinoid system has an effect on.
In fact, scientists discovered years ago that the main psychoactive constituent of cannabis, THC, acted on the endocannabinoid system to increase appetite in anorexia and even cancer patients.
Blood circulation
Of the two discovered endocannabinoids, 2-AG is one of the most important in the function of the brain, liver, and lungs. It produces arachidonic acid in these organs. This is used in the synthesis of prostaglandins. These perform functions such as blood pressure, blood clotting, and even your allergic inflammatory response.
Pain regulation
The endocannabinoid system plays a key role in intercellular communication. Furthermore, it plays a role in a wide range of physiological processes, such as pain perception. In fact, when your brain detects an inflammatory process or the presence of an injury, it immediately activates the release of endocannabinoids to reduce your suffering.
Memory and learning
Neuroscience has provided important information on these chemical compounds for years. One of the most important is that there are endocannabinoid receptors in the hippocampus and the cortex. These are the areas of your brain responsible for memory and learning.

The endocannabinoid system and pleasurable social experiences
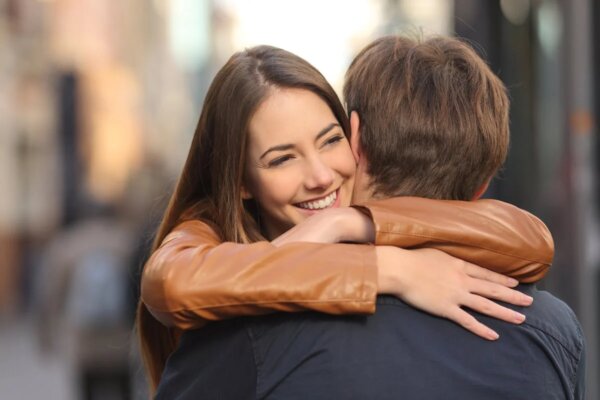
As we mentioned above, your entire body is flooded with these chemicals. However, a recent study from the University of Münster (Germany) discovered that AEA and 2-AG endocannabinoids are key to the pleasure you experience in everyday social relationships.
These endogenous chemicals facilitate the release of dopamine into your brain’s reward center every time you do something your brain interprets as socially positive. For example, a hug, having a cup of coffee with friends, taking a walk with your partner, and playing with your children.
This fills your bloodstream with these marijuana-like components that generate pleasure, well-being, and happiness. As you know, there’s no better way to reduce stress and anxiety in your life than spending time with those you love.
All cited sources were thoroughly reviewed by our team to ensure their quality, reliability, currency, and validity. The bibliography of this article was considered reliable and of academic or scientific accuracy.
- Redlich C et al (2021) The endocannabinoid system in humans: significant associations between anandamide, brain function during reward feedback and a personality measure of reward dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology, 46:1020–1027; https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-020-00870-x
- Lu, H. C., & Mackie, K. (2016). An Introduction to the Endogenous Cannabinoid System. Biological psychiatry, 79(7), 516–525. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.07.028
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








