Trigeminal Neuralgia: Characteristics and Treatment


Written and verified by the psychologist Gema Sánchez Cuevas
Many consider trigeminal neuralgia to be the most painful condition a human being can experience. Sometimes it’s even a direct cause of suicide. It comes from a disorder in a nerve in your brain that unleashes violent electrical shocks as a response to little, normal things: talking, eating, changes in temperature…
It’s not just a headache, or even a migraine. People who are unlucky enough to live with trigeminal neuralgia also know that painkillers don’t help. A lot of the time even morphine can’t relieve their pain.
When that happens, only antiepileptic drugs can help them live a somewhat functional life. What they get in in exchange, of course, are all the side effects that come along with those medications.
From the outside their pain might seem exaggerated. It’s not for no reason that some people call it the “suicide disease,” though. It was first classified in 1672, but there are examples of this illness that go much further back.
They describe it as one of the most paralyzing, intense kinds of pain anyone can go through. Today they estimate that trigeminal neuralgia affects between 8 and 12% of people. It may be a chronic illness, but there are still some treatments for it.
Trigeminal neuralgia involves extremely violent pain similar to an electric shock. It might last as little as two seconds or up to two hours, and it can reappear in multiple episodes over the course of a few weeks or even months.

What is trigeminal neuralgia?
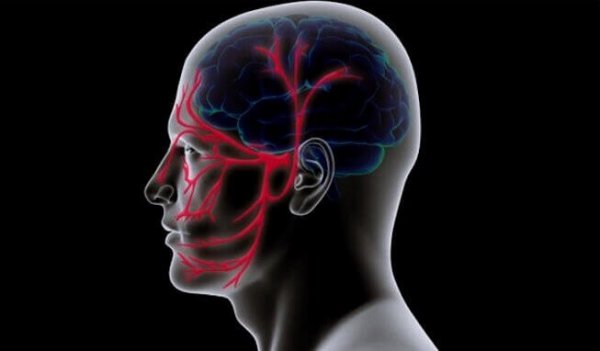
The root of trigeminal neuralgia is in the fifth out of our twelve cranial nerves. It’s the biggest of all the nerves in our head. Now we’ll look at its structure to give you a better understanding of how it radiates all that pain:
- This nerve has three branches. The first is the ophthalmic, or superior branch, which gives off a painful sensation that can go from your scalp to one side of your forehead, along with whichever eye is on that same side.
- The maxillary, or middle branch, stimulates your cheeks, upper jaw, upper lip, teeth, upper gums, and one side of your nose.
- Lastly there’s the mandibulary, or inferior branch. This one causes painful sensations in your lower jaw, teeth, lower lip, and lower gums.
People with trigeminal neuralgia will generally experience pain in one side of their face. But there’s also a rare condition called bilateral neuralgia that makes it worse. Basically it means that they’ll have trigeminal neuralgia on both sides of their head.
What symptoms does trigeminal neuralgia have?
The symptoms associated with trigeminal neuralgia vary between patients. One thing they all share are “trigger areas,” the regions that respond with intense pain when stimulated. The pain is like an intense electric shock that lasts seconds, minutes — up to two hours.
- Simple actions like touching or stroking your face can be painful.
- Changes in temperature, chewing, talking, and grinding your teeth can all trigger the paralyzing pain that goes with neuralgia.
- The pain follows a path that may go from your scalp to one eye, an ear, and all the way down to your jaw.
- After this intense electric shock, people with this illness usually can’t do anything for an hour or two. They won’t be able to eat, drink, or even open their eyes. They have to wait for the nerve to disinflame little by little.

Causes of trigeminal neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia doesn’t have one single cause. The condition actually has a wide range of associated factors. We’ll look at some now to better understand the complex reality behind this condition.
- Generally speaking, it is genetic.
- As MRI’s have shown, there’s often a blood vessel pushing the trigeminal nerve out of your brain stem. This compression then leads to deterioration of myelin, the protective layer of a nerve. That’s what makes it possible for those huge electric shocks to happen.
- Additionally, we know that facial or oral surgery and strokes caused by traumatic injuries can cause it.
- It’s also important to point out that the primary origin is often unknown. In other words, it’s almost impossible to know what exactly caused them to develop the illness.
Can it be treated?
We should remember that this neuropathic condition varies from person to person. There are people who go experience it for two months in a row, but then it goes away for awhile. Then there are people who go through it every day, and people who have it on both sides. Some have managed to control their triggers and enjoy a better quality of life.
That’s why a therapeutic approach needs to be customized to each person. But let’s look at some of the most common strategies:
- Antiepileptic medications are usually the most effective at treating trigeminal neuralgia. Drugs like carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, and gabapentin are the most common.
- Tricyclic antidepressants like amitriptyline and nortriptyline are a common treatment for pain relief in this illness.
A last resort: surgery
When medications doesn’t work, the only other option is surgery. Here are the different options patients have when that happens:
- Rhizotomy: temporarily damaging specific nerve tissues so they don’t cause pain.
- Glycerol injection: an outpatient procedure involving the tissues around your trigeminal nerve. This treatment takes at least two years.
- Radiofrequency lesioning: an outpatient procedure where they use an electrode to damage the nerve tissues causing the pain. It’s temporary, like rhizotomy.
- Microvascular decompression: the most invasive (and effective) of all the surgeries. First they make a small hole in the mastoid bone behind your ear. Then they use a tiny balloon to move the blood vessel pushing against your trigeminal nerve away.
So as you can see, there are a lot of different ways to deal with trigeminal neuralgia. It affects between 8 and 12% of the population, and we also know that around 70 to 80% of patients respond well to medication. That means they’ll never have to undergo surgery.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








