GABA: The Neurotransmitter of Peace and Relaxation
Do you feel excited, irritable, or sad for no apparent reason? Do you feel that way constantly? Although there can be many explanations for this, there’s a possibility that your brain may be suffering from low levels of certain substances. Our brain uses up to 100 different neurotransmitters and GABA is one of them. This is the neurotransmitter of peace and relaxation.
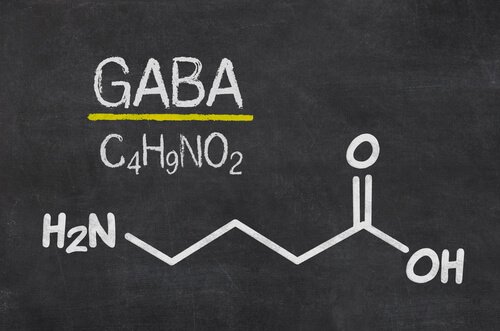
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an amino acid and neurotransmitter that regulates brain excitability by inhibiting an excessive firing of neurons, which leads to a feeling of calm. Having adequate GABA levels can reduce stress, make you feel less anxious, and reduce the likelihood of different health issues.
What is GABA and what does it do?
Gamma-aminobutyric acid is one of the most important neurotransmitters. Now, neurotransmitters are basically the chemicals that brain cells use to communicate with each other. In fact, GABA is the most frequent inhibitory neurotransmitter. Inhibitory neurotransmitters decrease the probability of discharge of a nerve impulse.
Its main function as an inhibitory neurotransmitter is to slow down brain activity. Additionally, it’s involved in vision, sleep, muscle tone, and motor control. It’s also widely distributed both inside and outside the central nervous system. It’s found in the intestines, stomach, bladder, lungs, liver, skin, spleen, muscles, kidneys, pancreas, and reproductive organs.
The diseases and disorders that are related to GABA dysfunction include autism, bipolar disorder, depression, schizophrenia, epilepsy, fibromyalgia, meningitis, some kinds of dementia (Alzheimer’s, Lewy body disease, frontotemporal dementia), and some intestinal disorders (Crohn’s disease, colorectal cancer, IBS, ulcerative colitis). In addition, diseases characterized by involuntary movements such as Parkinson’s, tardive dyskinesia, and Huntington’s disease are also associated with low levels of this neurotransmitter.
One of the most important functions of GABA is minimizing stress and anxiety. Low levels of this neurotransmitter lead to an increase in feelings of anxiety and sensitivity to stimulation. Nature Magazine published an article that states that this neurotransmitter can decrease those unwanted thoughts that feed stress, anxiety, depression, and other psychological disorders.
Gamma-aminobutyric acid also affects brain activity because it alters brainwave patterns. The presence of this neurotransmitter increases those brain waves associated with a relaxed state (alpha waves) and decreases those associated with stress and anxiety (beta waves).
The balance of brain activity
To be able to talk about how gamma-aminobutyric acid works, we have to keep another neurotransmitter in mind: L-glutamate. This neurotransmitter is a natural byproduct of energy production in the brain. L-glutamate is actually one of the products of the metabolization of glucose in the brain, making it significantly important.
These two neurotransmitters are complementary and opposite. L-glutamate, as the main excitatory neurotransmitter, balances the inhibitory effects of GABA. Excitatory neurotransmitters increase the probability of discharge of a nerve impulse. While GABA slows down brain activity, L-glutamate accelerates it.
Both of them work together to control brain activity. They work as a team and can also convert into the other. L-glutamate is the precursor of GABA, which, in turn, can be recycled into L-glutamate as needed.
Are your GABA levels low?
In most cases, GABA dysfunction can be directly attributed to a person’s lifestyle. According to Dr. Datis Kharrazian, a researcher at Harvard Medical School, too much stress, a poor diet, lack of sleep, too much caffeine, and gluten intolerance are some of the causes of a GABA “dysfunction”.
Also, it’s important to keep in mind that intestinal bacteria produce this neurotransmitter. Dysbiosis (an imbalance between good and bad intestinal bacteria) can cause a significant reduction in GABA production.
In addition, we must note that excess L-glutamine is converted into GABA with the help of vitamin B6 and an enzyme called glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). Now, a vitamin B6 deficiency or an autoimmune reaction can interfere with the production of this neurotransmitter. An autoimmune disorders, diabetes, gluten intolerance, celiac disease, and Hashimoto’s disease may be the causes of this autoimmune reaction.
On the other hand, keep in mind that there are a lot of internal chemical changes that can have an influence on the L-glutamate-GABA balance. Also, when it comes to consumer substances, caffeine inhibits GABA activity, whereas alcohol and tranquilizers increase it.

How to increase GABA levels
There are GABA supplements that contain a synthetic form of this neurotransmitter. However, there is controversy over whether said supplements actually work. Something that’s still unknown is if GABA will reach the brain in adequate amounts to have the effect it’d normally have if taken as a supplement. Nonetheless, some people have claimed that these supplements are very useful.
Additionally, there isn’t an established dosage of these supplements nor enough research on their possible side effects. In fact, there’s actually no real research on the safety of these supplements.
However, there are many other natural ways to maintain healthy GABA levels. One of them is food. Researchers have analyzed the GABA contents of a wide variety of foods such as whole-grain rice, brown rice sprouts, barley sprouts, beans, corn, brown rice, spinach, potatoes, sweet potatoes, kale, and chestnuts.
Also, a Biosciences Institute at University College Cork in Ireland study revealed that probiotic foods increase gamma-aminobutyric acid. Foods such as yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain the bacterial strains that produce GABA.
If you’re concerned about your GABA levels, it’s important to minimize your caffeine intake, as it inhibits the ability of this neurotransmitter to bind to its receptors. Instead, you can drink tea, which contains less caffeine and, in addition, contains the amino acid L-theanine that increases the production of this neurotransmitter.
Another very effective way to increase your GABA levels is through exercise. Any type of physical exercise increases the levels of this neurotransmitter, yoga being the most prominent one. Fun fact: the levels of this neurotransmitter in the brain can increase up to 27% after a single yoga session.
This text is provided for informational purposes only and does not replace consultation with a professional. If in doubt, consult your specialist.








